 In many workgroup environments, a client version of Windows is found used a “server”. Also, there is often no physical security of this “server” in such environments. This makes it very easy for a simple user to log on to the machine, even though he/she should not. This can be prevented, as described below. Please note that must have administrative privileges to do this.
In many workgroup environments, a client version of Windows is found used a “server”. Also, there is often no physical security of this “server” in such environments. This makes it very easy for a simple user to log on to the machine, even though he/she should not. This can be prevented, as described below. Please note that must have administrative privileges to do this.
How do I do that?
- Logon as an administrator.
- Open Computer Management Console (
%windir%/system32/compmgmt.msc /s).
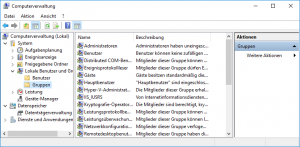
- Change to [System > Local Users and Groups > Groups].
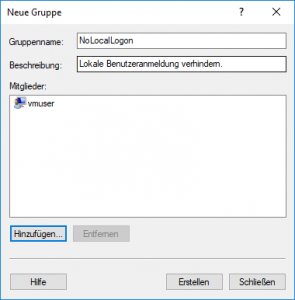
- Create a new group having a suitable name, e.g. NoLocalLogon; optionally enter a description.
- Assign the (existing) local users, for which a local logon should be prevented, to this group.
- Open the Group Policy Editor (
%windir%/system32/gpedit.msc /s) using [Start > Run]. - Change to [Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > User Rights Assignment].
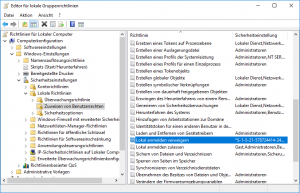
- Open settings for local group policy by double clicking [Deny log on locally] to add the created group from above:
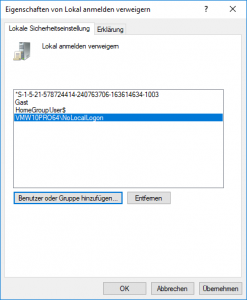
- Press [Add User or Group] to select the group to be added.
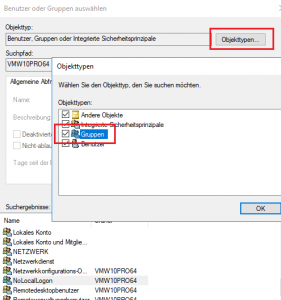
- Ensure that groups are part of the search result: press [Object Types] and enabled option [Groups]; press [OK] save changes.
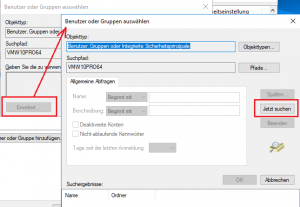
- To search the group press [Extended] to open the search dialog and press [Search now] to start searching; select the group and press [OK] to proceed.
- Press [OK] to add the selected group to the policy.
- Press [Add User or Group] to select the group to be added.
- Press [OK] to save changes on group policy.
What has just happened?
The new configuration will take effect immediately. If a user, who is a member of the created group, tries to log on locally to the computer, he/she will receive a message and the login process will not be prevented. However, it is still possible to log on to shares (e.g. to connect network drives or printers).
Limitations
This configuration is not possible in the Home editions of Windows.


